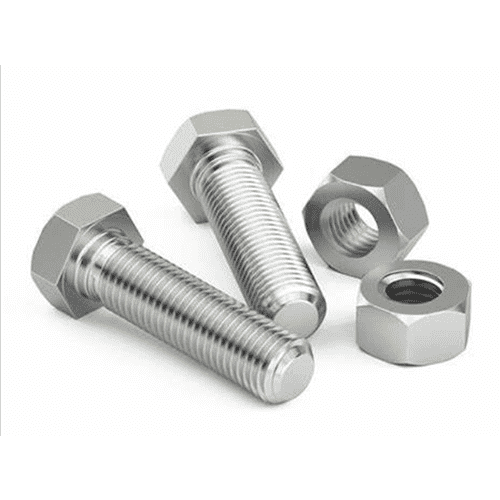
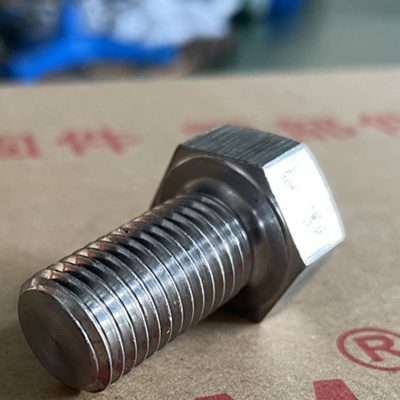
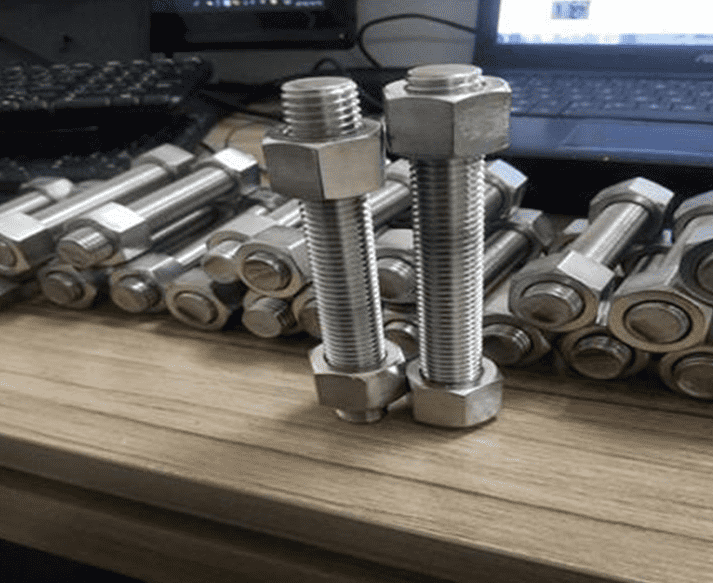
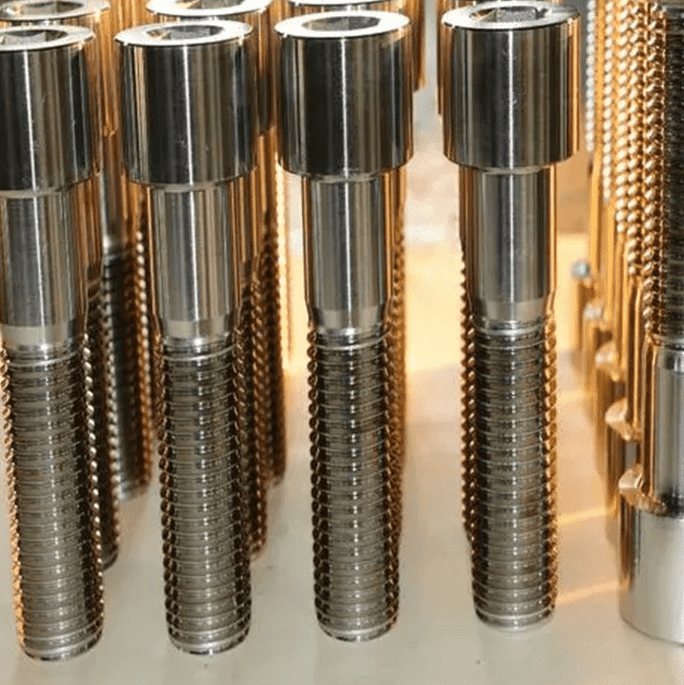
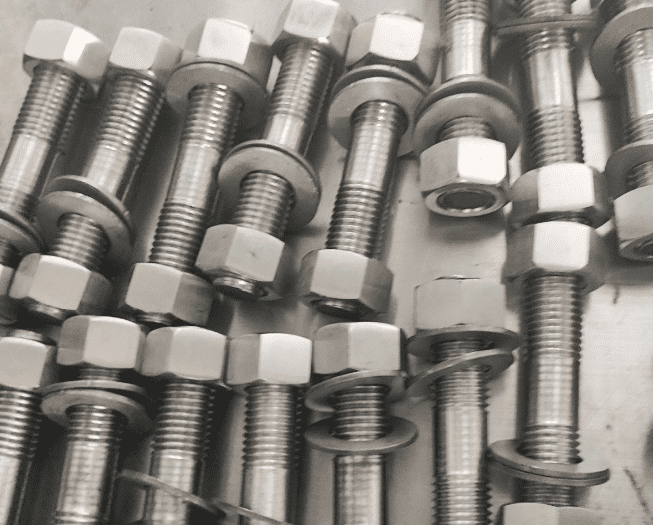
Heavy-duty bolts differ significantly from regular bolts in several dimensions. First of all, from the material point of view, heavy-duty bolts tend to use high-strength alloy steel or stainless steel to ensure their stability and durability under high loads and extreme conditions; while ordinary bolts mostly use low-carbon steel or stainless steel, which is suitable for Low load, low temperature environment. Secondly, in terms of strength, the tensile strength and shear force of heavy-duty bolts are far higher than ordinary bolts, and they are key connectors to support large machinery and equipment. Structurally, the design of heavy-duty bolts is more complex and contains multiple parts to enhance load-bearing and protect threads; while ordinary bolts are relatively simple and mainly consist of threads and nuts. In terms of application fields, heavy-duty bolts are widely used in heavy-duty industries such as bridges, construction, and machinery; ordinary bolts are more common in daily fields such as automobiles, electrical appliances, and pipelines. Finally, in terms of environmental protection, when using heavy-duty bolts, more consideration must be given to the damage to structures and vibration and noise control; ordinary bolts have lower requirements in this regard. To sum up, choosing the right bolt type is crucial to improving work efficiency and service life.
| All Material for heavy hex bolts | ||||
| Hastelloy C276 | Duplex 2205 | A193 B8 | SS304 | Inconel600 |
| Hastelloy C22 | Duplex S31803 | B193 B8M | SS316 | Inconel601 |
| Hastelloy C4 | Super duplex S32750 | Alloy59 | SS316L | Incoloy718 |
| Monel400 | Super duplex 2507 | Alloy20 | Stainless steel 18-8 | Incoloy800H |
| Monelk500 | 904L | 309S | SS321 | Incoloy800 |
| Nimonic 80A | Alloy 926 -UNS N08926 | 310S | 317L | Incoloy825 |